Osteoporosis means porous bones; it is a disease in which the density and quality of bone are reduced.
As bones become fragile they break more easily. These are known as fragility fractures and occur most frequently in the vertebrae (spine), wrist and hip.
Wrists
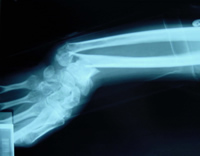
Bone loss in osteoporosis occurs silently and progressively without symptoms, until the first fracture occurs; usually a wrist fracture.
Broken wrists often occur in middle aged women who have put out their arm to break a fall.
Hips
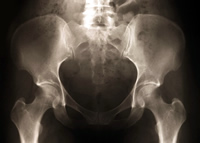
The majority of hip fractures occur as a result of a fall from standing height; most commonly in women and men in their late 70s or 80s.
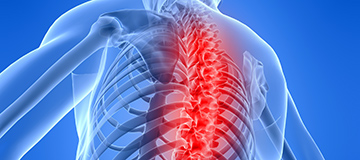
Spinal Bones
Spine fractures (vertebrae) usually occur in the lower back (lumbar) or upper area (thoracic) of the spine.
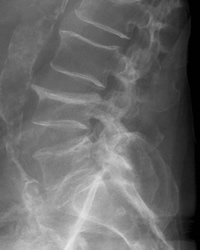
Bones become squashed or compressed because of their reduced strength, leading to loss of height and deformity (curvature of the spine).
Spinal fractures can cause intense back pain.
While our genes are vital in deciding the potential size and strength of our skeleton, we cannot choose our parents. The way you live your life (not smoking, safe drinking, regular weight bearing exercise and eating a well balanced diet), can also play an important part in reducing your risk of breaking a bone.
1 in 2 women and 1 in 5 men over the age of 50 will suffer a fragility fracture in their remaining lifetime.